Learning from Error : assignment to expression with array type.
Error Learning : assignment to expression with array type
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
char course_name[20];
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node Node;
int main(void) {
Node *head = malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->course_name = "Opearating system";
head->next = NULL;
int i;
int number; // the number of course
printf("請輸入課程數量: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
Node *current = head;
for(i = 1; i <= number; i++){
current->next = malloc(sizeof(Node));
char name[20]; // string
printf("請輸入課程名稱: ");
scanf("%s", name);
current->course_name = name;
current = current -> next;
current -> next = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
**Error1 : assignment to expression with array type (line 13, line 29)**
Reason : You cannot directly assign to an array.
Solution : You need to use strcpy() to copy into the array.
-
What is LHS and RHS?
Address1 is on the left hand side (LHS), and “Address2” is on the right hand side (RHS).if(Address1 == Address2){...} else{...} -
Difference between assignment and initialization.
int a; // declare a variable int b = 5; // declare and initialize a variable almost at the same momentint a; // declare a variable a = 3; // assign a variable
雖然看似沒有不同,但實際compiler轉譯到assembler language是代表不同的assembly code。如果使用在陣列上,那麼用第二個方法就會出現錯誤(直接assign到在LHS的array變數就會出錯),必須使用 strcpy() (使用 strcpy()需引入標頭檔 #include<string.h>)
除了array以外,struct結構型態、const常數修飾子,都不能這樣使用
<Error example 1> array
char name[] = "Sophie"; // is validchar name[]; name[]= "Sophie"; // is not valid
<Error example 2> struct
struct classmate student1 = {.name ="Jack", .no ="34567"}; // valid
struct classmate student1;
student1 = {.name ="Jack", .no ="34567"}; // is not valid
<Error example 3> const
const int a = 5; // is validconst int a; a = 5; // is not valid
Error 2
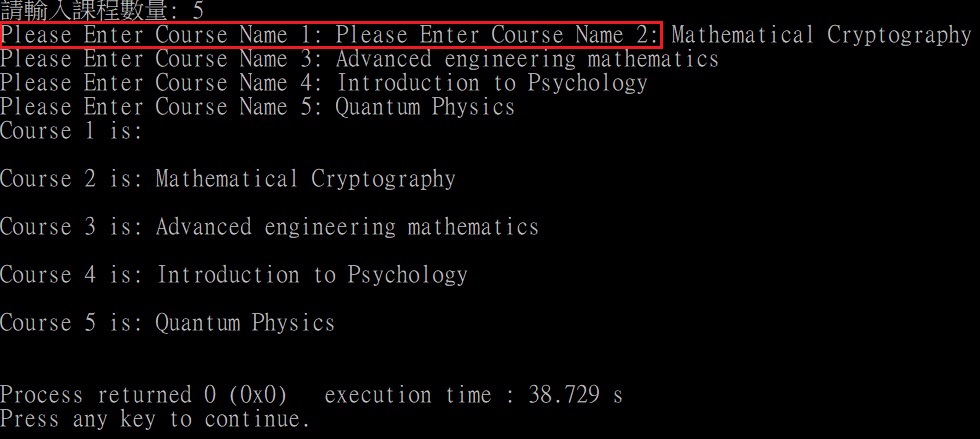
Solution Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct node{
char course_name[50];
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node Node;
int main(void) {
Node *head = malloc(sizeof(Node));
// head->course_name = "CS course"; //error
strcpy(head->course_name, "CS course");
head->next = NULL;
int i;
int number; // the number of course
printf("請輸入課程數量: ");
scanf("%d\n", &number);
/* 輸入值時,會按Enter(換行字元'\n'),來結束number的輸入,置入到buffer中
* 若沒有再輸入值當中加入'\n',會被fgets當作輸入用,
* 因此在輸入course name時,會少一次輸入
* 所以在%d加上'\n'字元讓scanf吃掉enter('\n'換行字元)
*/
Node *current = head;
for(i = 1; i <= number; i++){
current->next = malloc(sizeof(Node));
char name[50]; // string
printf("Please Enter Course Name %d\n: ", i);
fgets(name, sizeof(name), stdin);
// 1. scanf("%s", name); 不使用這種是因為打空白直接算另一個字串
// 2. gets(name) 不使用這種是因為也有一樣的問題
// current->course_name = name // error
strcpy(current->course_name, name);
current = current -> next;
current -> next = NULL;
}
// print all course and clear memory
current = head;
Node *temp; // temporary and delete
i = 1;
while(current != NULL && i <= number){
printf("Course %d is: %s\n", i, current->course_name );
temp = current->next;
free(current);
current = temp;
i++;
}
head = NULL;
return 0;
}